|
Tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears when there is no external source of sound. It can be a challenging condition to treat, as it can have various underlying causes, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. However, there are several strategies you can try to manage and potentially reduce the symptoms of tinnitus:
Hearing Aids: If you have hearing loss in addition to tinnitus, a professional hearing aid fitting typically helps by amplifying external sounds to make the tinnitus less noticeable. Clinical evidence shows external sounds can provide activation of the auditory nervous system. Activation of the auditory nervous system reduces the tinnitus perception. It may also elicit expression of neural plasticity . Neural plasticity refers to the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. Neural plasticity may reprogram the auditory nervous system and thereby have a long-term beneficial effect on tinnitus by restoring neural function. Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you're experiencing tinnitus, it's essential to consult a hearing instrument specialist, audiologist or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist to determine the underlying cause. They can help identify potential medical issues that may be contributing to your tinnitus. Address Underlying Causes: If tinnitus is related to an underlying medical condition, such as an ear infection or high blood pressure, treating these issues may alleviate tinnitus. Medications: In some cases, tinnitus may be a side effect of certain medications. Discuss your medications with a healthcare professional, and they may be able to adjust your prescription. Noise Masking: Use white noise machines, fans, or calming music to mask the tinnitus sounds, making them less noticeable. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT): TRT is a form of cognitive-behavioral therapy designed to help you habituate to the sounds of tinnitus. It involves counseling and sound therapy.
It's essential to remember that tinnitus is a complex and often persistent condition, and there is no guaranteed cure. What works for one person may not work for another. Your healthcare provider can help you develop a personalized treatment plan based on the specific cause and impact of your tinnitus. Patience and persistence are key when managing tinnitus. Why are my ears ringing? Tinnitus, the sensation of ringing or noise in the ears when there is no external source of sound, can have various causes. Common reasons for tinnitus include:
Remember that while there may not always be a cure for tinnitus, various strategies, as mentioned in the previous response, can help you manage and reduce its impact on your life.
0 Comments
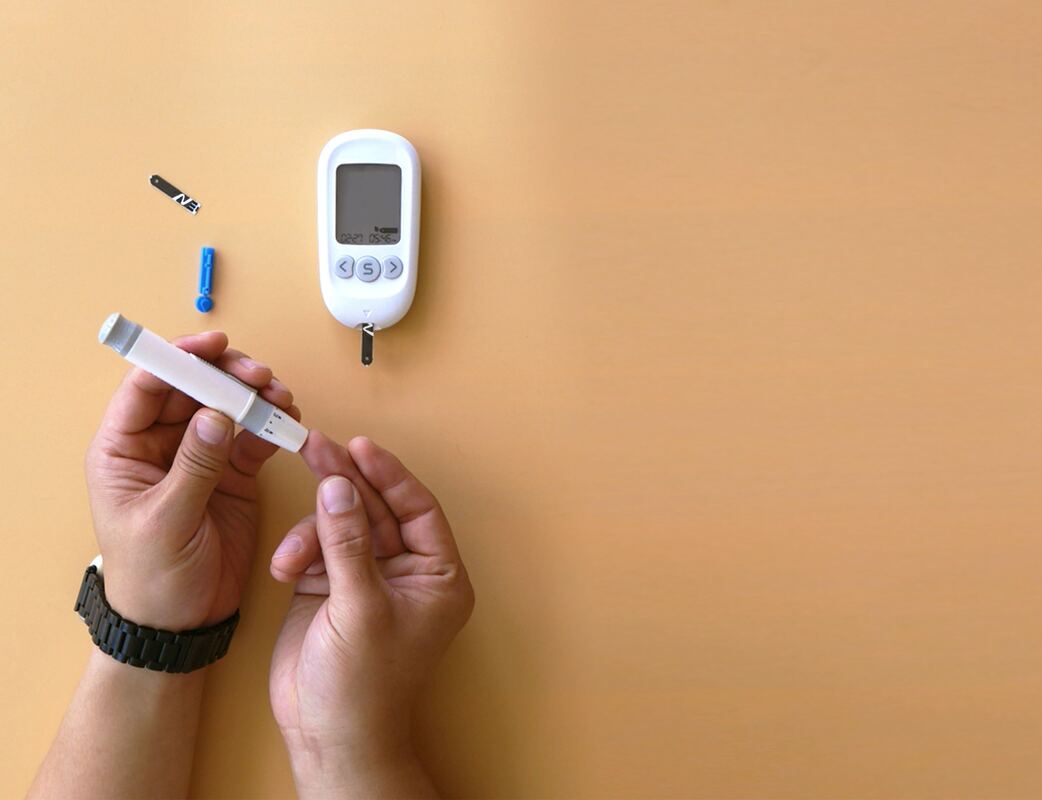
When your blood sugar levels are not regulated, you may experience hearing loss.
Diabetes and hearing loss are common health issues among American adults. There have been reports from nearly 15% of adults in the U.S. (37.5 million) who said they experienced problems with their hearing. Symptoms of hearing loss generally worsen as a person ages. Roughly 25% of people between 65 and 74 years old have this condition. About 50% of people, at least 75 years old, sustain disabling hearing loss. There is an overlap among patients with both diabetes and hearing loss. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), patients with diabetes are twice as likely to have hearing loss than patients who do not have diabetes. In the U.S., patients with prediabetes blood glucose levels are more likely to have a 30% higher rate of hearing loss than patients with average blood glucose levels. Diabetes and Hearing Loss can lead to Sensory Damage. Your nervous system can become damaged from unmanaged diabetes. That can impact your whole body. A common symptom is the inability to hear high and low frequencies. Other risk factors may include heart disease, low HDL cholesterol, peripheral neuropathy, and overall poor health. If you have diabetes and chronic diseases, you should get a hearing test. Some medications related to diabetes affect a patient’s overall health, which can negatively impact their hearing. There are some things you can do to curb this problem.
How can Diabetes lead to Falls? Falls are another thing to worry about if you have diabetes and hearing loss. The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, is the sensory system that gives the fundamental sense of balance and spatial orientation on a person’s movement with balance -. The vestibular system can become damaged due to diabetes. The top complaint from patients over 70 years old, with diabetes and hearing loss, is vertigo. Hearing problems that remain untreated can harm relationships, whether they are personal or professional. These are some reasons why taking care of both diabetes and your hearing should be a priority. Better hearing can lead to better overall health by giving you more energy to live your life. Contact Northumberland Hearing Center for a hearing exam and consultation with our hearing care professionals. |
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
